Share this
Encountering a Cyberthreat: What Should You Do, And Why Is It So Easy to Fall For?
by Gregg Jones on Feb 1, 2022 12:00:00 AM
Threats can be hard to spot. When you’re not on the lookout for what might be the entrypoint for a data breach, you’re more likely to miss it. And oftentimes, threat actors are good at reaching you when you’re vulnerable—and when you’re expecting something.
In this post, I’ll paint you a picture using a recent threat we discovered.
A Normal Day:
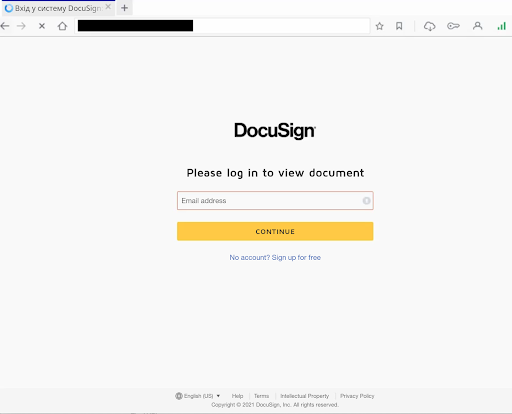
So you’re working on closing a large contract with a company, and you expect to hear back from them shortly. Suddenly, you get a ping as a new email enters your inbox. You tab over from the latest and greatest trends in dog-based TikToks to see what should be the email you’ve been expecting. You click the link and are brought to a DocuSign page and are prompted to put in your email.
Now let’s pump the breaks. Could something be wrong here?
Recently, our Data Science Team (DSI) encountered a threat that had embedded itself on a reputable site.
The Case:
This particular phish had breached the web infrastructure of this site, and established a falsified web page.
Our DSI team examined some of the history behind this original site, and was able to see for the most part that it looks benign. However there were some flags that led us to a slew of non-unique .ru domains and the redirect in question.
These domains included hot keywords such as “signup”, “signnow”, “counter”, and “maildrop” among others along with randomized domain names.
This is not the normal DocuSign page. This page essentially looks for unsuspecting emails/login information to get access to proper logins. In addition, it's not typical for a cyrillic redirect to show up in your browser—unless you have that as a default language—and even from there, it’s missing a few components of a typical DocuSign login. A trusted DocuSign login page will have “Powered by DocuSign” in the lower left, an up-to-date Copyright date (this threat was found in 2022, but the date was still 2021), and some of the text in the footer is slightly different.
.png)
What Can I Do?
How can you protect yourself? Always verify your links, and always look at who’s sending the email. Sometimes it can be tricky, but when expecting something that has vital information attached, whether it be a bank statement, a document to sign, or something asking for a unique login, it may be worth going to the actual site and entering your information in a fresh browser session. An extra two minutes could save you a world of trouble later.
We are continuing to keep an eye on this particular case, and are also looking for similar cases.
If you have a lead, feel free to reach out! We love making your web experience safer.
Share this
 Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
The term “artificial intelligence (AI)” was first coined in 1956. While progress stalled for many years, we can thank IBM for sparking real interest in AI as viable technology: First in 1997 when the computer Deep Blue defeated a chess champion and again in 2011 when Watson won Jeopardy!
 The Mind Games Behind Cyber Attacks
The Mind Games Behind Cyber Attacks
Hackers have long understood that the most sophisticated firewall is no match for a well-placed psychological trick. While many focus on the technical prowess of cybercriminals, the real magic often lies in their ability to manipulate human behavior. By exploiting our natural tendencies and cognitive biases, hackers can slip past even the most robust security systems. It's not just about cracking codes; it's about cracking the human psyche.
 AI and Cybersecurity Risks: Why DNS Filtering is Critical for AI-Driven Workplaces
AI and Cybersecurity Risks: Why DNS Filtering is Critical for AI-Driven Workplaces
Artificial intelligence is transforming business operations, automating everything from customer service to data analysis. But with these advancements come new security challenges. AI-driven cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated, enabling attackers to automate phishing campaigns, generate malware, and exfiltrate sensitive data at scale. Without proper safeguards, AI tools can unintentionally leak corporate secrets or connect to malicious ...


