Share this
Unmasking Roaming Mantis: The Mobile Malware Menace You Need to Know
by Jacob Phillips on Mar 22, 2023 4:13:00 PM
Roaming Mantis, also known as Shaoye, is a DNS hijacking malware originating in Japan that was first discovered by the cybersecurity firm, Kasperksy, in 2018 after media reports of hijacked DNS settings on routers in Japan. Roaming Mantis started off as a banking Trojan—a type of malware that attempts to steal credentials from financial institutions’ clients and gain access to their financial information.
Roaming Mantis has now expanded beyond Asia into Europe, specifically France and Germany. According to Kaspersky Security Network statistics, from September to December 2022, the highest number of Wroba.o (Roaming Mantis) malware attacks were in France (54.4%), Japan (12.1%), and the U.S. (10.1%).
The staggering percentage of malware attacks in France could largely be attributed to France's large mobile device user base, with over 75 million mobile phone users, as reported by ARCEP in 2021, which makes it an attractive target. Additionally, France's strategic location in Western Europe, sharing borders with several other countries—including Germany, Switzerland, and Italy—makes it an appealing target for cybercriminals who seek to spread their malware across borders.
Behind the Scenes of Roaming Mantis: Understanding How This Mobile Malware Threat Operates
The Sneaky Scheme: Initial infection starts when the victim is lured into downloading a malicious app from either the App Store, a malicious website, or through social engineering tactics such as phishing emails.
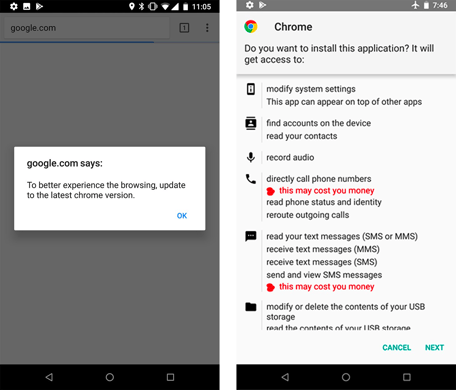
Hijacking Your Way In: Once the malicious app is downloaded onto the victim’s device, the malware changes the device’s settings to redirect the victim’s internet traffic to malicious servers controlled by the attackers. This is accomplished by modifying the DNS server settings in the device’s network settings.
The Trojan Horse Within: Once traffic is redirected, the attackers can install additional malware on the victims device. This can include keyloggers, spyware, or other types of malware that can steal sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, and financial data.
Hook, Line, and Sinker: How Roaming Mantis Reels in Victims with Phishing Emails
Behind the Bait: The attackers send a phishing email that appears to be from a legitimate source, such as a bank, social media platform, or an online retailer. The email will contain a link that will direct the victim to a fake login page.
Click, Click, Infected: If the victim clicks the link, they are taken to a fake login page that is identical to the legitimate website. The victim may not realize they are on a fake website and enter their login credentials.
Hooked and Hacked: When the victim enters in their login credentials, the attackers collect the information and use it to gain access to the victims account. This gives the attackers access to sensitive information, such as personal and financial data.
How Roaming Mantis Allows Attackers to Take Over Your Device
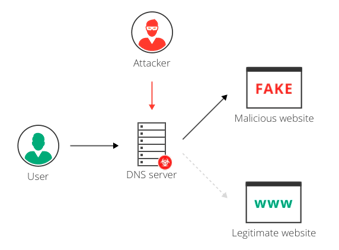
Uninvited Guest: After a victim’s device has been infected with the Roaming Mantis malware, attackers use the injection to gain remote access to the device. This is done by using DNS hijacking, which establishes a connection between the victim’s device and a remote server controlled by the attackers without the victim knowing.
Seizing Control: Once the attackers have remote access, they can take control of the victim’s device. This allows them to carry out a wide range of malicious activities, including stealing sensitive information, installing additional software, or carrying out attacks on other devices connected to the same network as the victim’s device. Using remote access with Roaming Mantis malware is a big advantage for the attackers because they are able to use the victims device as a launch point for further attacks.
Eliminating Roaming Mantis: How to Banish the Mobile Malware Menace
Fortify Your Defenses
Using reputable antivirus software to scan your device frequently and detecting any malware infections can go a long way in guaranteeing your device will never have to worry about the Roaming Mantis malware in the first place.
However, what makes cybersecurity policies so effective is the installment of layers. Antivirus software is great but you will also want to use a secure DNS service and a VPN as well. DNS hijacking is a common technique used by Roaming Mantis, and other malware to infect devices. Use a DNS service, such as DNSFilter, to prevent malicious DNS requests and protect against DNS hijacking.
Your VPN can help protect your device and data by encrypting your internet traffic and hiding your IP address. This can prevent attackers from intercepting your internet traffic and stealing sensitive information.
Last but not least, make sure your device and software are both up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates. This can help prevent future malware infections and keep your device secure. You can do this by ensuring you always update your device whenever prompted and update the apps on your phone whenever you see the notification to do so.
Malware Meltdown
If your device is infected, no need to panic. There are methods you can take to help remediate the and take back control of your device again.
Disconnect Your Device: If you suspect your device has been infected with the Roaming Mantis malware, the first step is to disconnect your device from the internet and any other network immediately. This will ensure that no other devices have the potential to be infected from your device as a launch point.
Sweeping Away the Malware: If your device is infected with Roaming Mantis, you may need to remove any malicious apps that were installed without your permission. This can typically be done through your device’s app settings or through a reputable antivirus program.
Burn the Paper Trail: Whether you entered your login credentials or not, if you were infected with malicious software like Roaming Mantis, it is best practice to change them immediately after the malware. You never know what the malware was able to grab or not so it’s safe to assume the worst. This will include passwords, PINs, and any other login information stored on the device or mentioned in services accessible by the device.
DNSFilter: Your Secret Weapon Against Roaming Mantis Malware on Mobile Devices
Roaming Mantis is a type of malware that primarily targets mobile devices and can be used to steal sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, and financial information. DNSFilter can help combat against Roaming Mantis by blocking access to malicious domains and IP addresses that the malware uses to communicate with its command and control (C&C) servers.
There are plenty of other features that you can utilize using DNSFilter to also combat against Roaming Mantis and future malware attacks:
Threat Intelligence Feeds: DNSFilter ingests threat intelligence feeds to identify domains and IP addresses associated with Roaming Mantis. These feeds are constantly updated with the latest information on malware are used to block access to malicious sites.
DNS-Based Blocking: DNS-based blocking is used to prevent devices from accessing malicious domains and IP addresses associated with malware such as Roaming Mantis. This method blocks requests at the DNS level before they reach the device, which helps to protect against malware infections.
DNS Traffic Monitoring: DNSFilter can monitor DNS traffic for suspicious activity that could be indicative of Roaming Mantis or other types of Malware. For example, it can look for devices that are making multiple requests to known malicious domains or IP addresses.
Machine Learning AI: DNSFilter leverages machine learning to identify new and emerging threats, including variants of Roaming Mantis. Machine learning algorithms can analyze patterns in DNS traffic to identify suspicious behavior and block access to potentially malicious sites.
By implementing these measures, DNSFilter protects against Roaming Mantis and other types of malware. However, it is important to note that DNS-based protection is just one layer of defense and should be used in conjunction with other security measures, such as antivirus software and firewalls.
Share this
 Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
The term “artificial intelligence (AI)” was first coined in 1956. While progress stalled for many years, we can thank IBM for sparking real interest in AI as viable technology: First in 1997 when the computer Deep Blue defeated a chess champion and again in 2011 when Watson won Jeopardy!
 The Mind Games Behind Cyber Attacks
The Mind Games Behind Cyber Attacks
Hackers have long understood that the most sophisticated firewall is no match for a well-placed psychological trick. While many focus on the technical prowess of cybercriminals, the real magic often lies in their ability to manipulate human behavior. By exploiting our natural tendencies and cognitive biases, hackers can slip past even the most robust security systems. It's not just about cracking codes; it's about cracking the human psyche.
 AI and Cybersecurity Risks: Why DNS Filtering is Critical for AI-Driven Workplaces
AI and Cybersecurity Risks: Why DNS Filtering is Critical for AI-Driven Workplaces
Artificial intelligence is transforming business operations, automating everything from customer service to data analysis. But with these advancements come new security challenges. AI-driven cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated, enabling attackers to automate phishing campaigns, generate malware, and exfiltrate sensitive data at scale. Without proper safeguards, AI tools can unintentionally leak corporate secrets or connect to malicious ...


